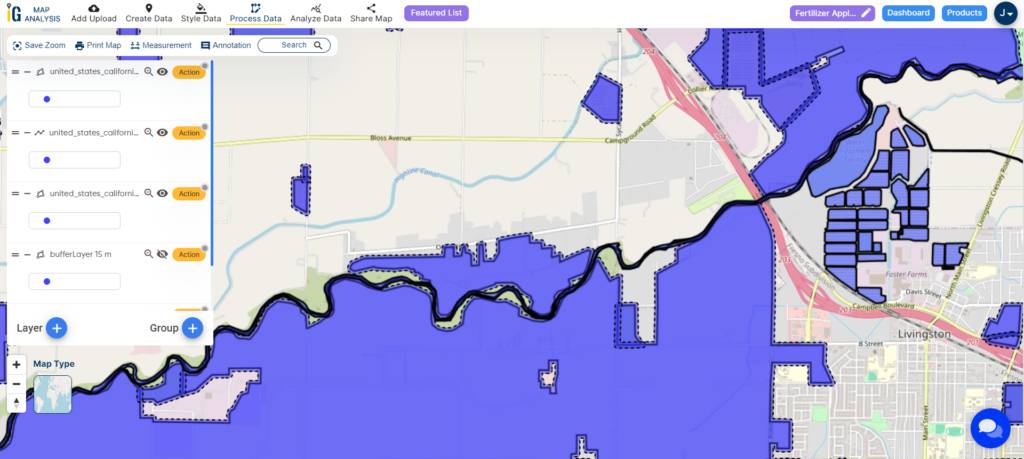
In the world of farming, we’re on a mission to do things in a smarter and more eco-friendly way. We’re diving into how we can be super careful about using fertilizers near water, and we’ve got a helpful tool called MAPOG Map Analysis to guide us. This tool uses GIS in Precision Agriculture and create safe zones around our fields. We’re aiming for a sweet spot where we can grow great crops without harming our precious water. This is all about finding a balance, and it’s something farmers are really putting effort into. Stick around as we explore how using technology like MAPOG is making farming better for the environment.
Key Concept for using GIS in Precision Agriculture
The main idea here is to find a smart and eco-friendly way to use fertilizers in farming, especially near water. We’re using a tool called MAPOG Map Analysis to help us create safe zones around our fields. The big goal is to grow great crops without hurting our precious water. It’s all about finding the right balance, and farmers are using technology like MAPOG to make sure they’re doing it in a way that’s good for the environment.
Moreover, for those interested in diving deeper, the dataset used for this analysis can be found at the end of this article. This dataset serves as the foundation for the spatial analysis conducted with MAPOG Map Analysis, shedding light on the practical application of these sustainable farming practices.
The following steps outline the process:
Step 1: Add Layer
- Open the GIS Data tool used for analysis.
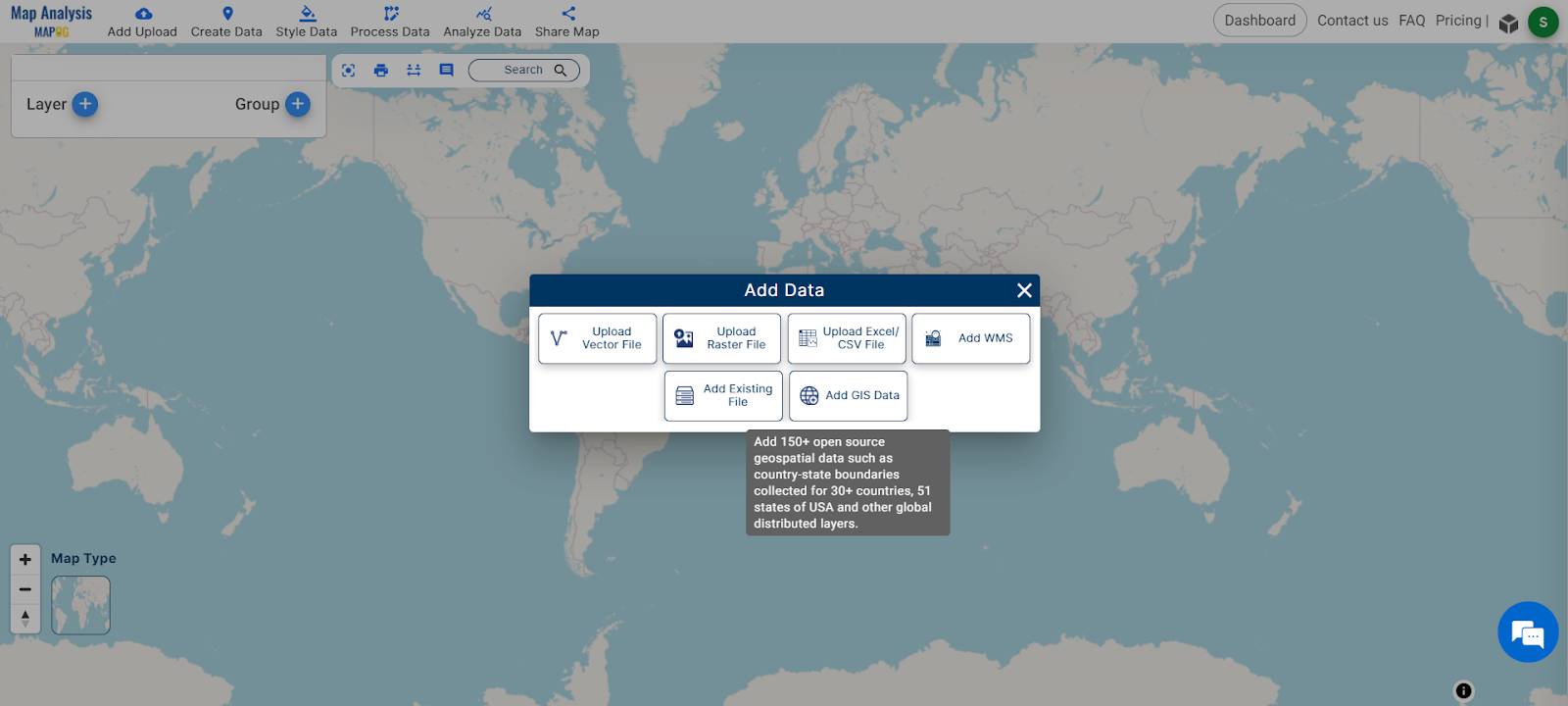
- Navigate to the desired country for analysis.
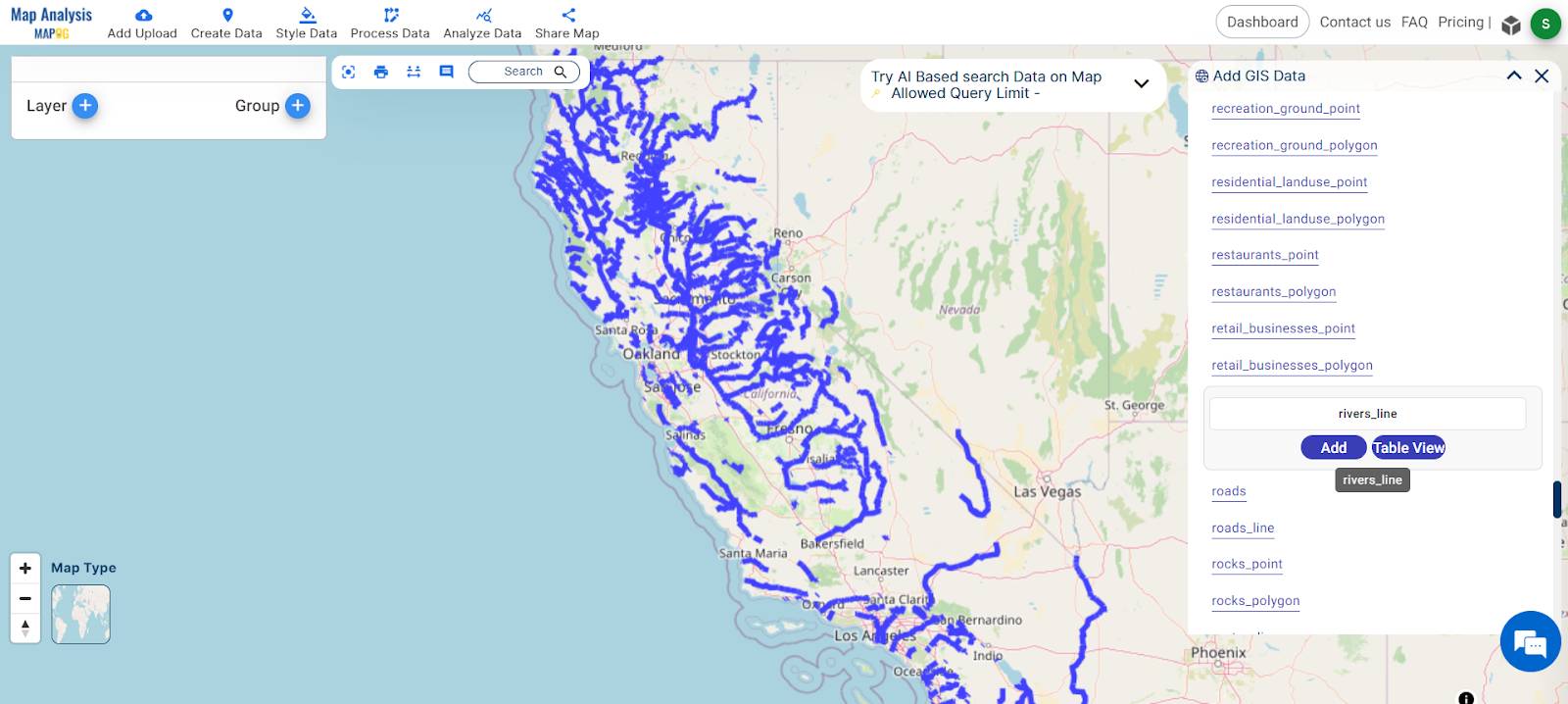
- Select the River Line, Agricultural Polygon and Lakes Polygon data layers for analysis.
- Add all data layers by clicking the “ADD” button.
- You can use the Crop tool to define and select specific areas of interest for analysis, enabling a focus on particular regions or segments based on your requirements.
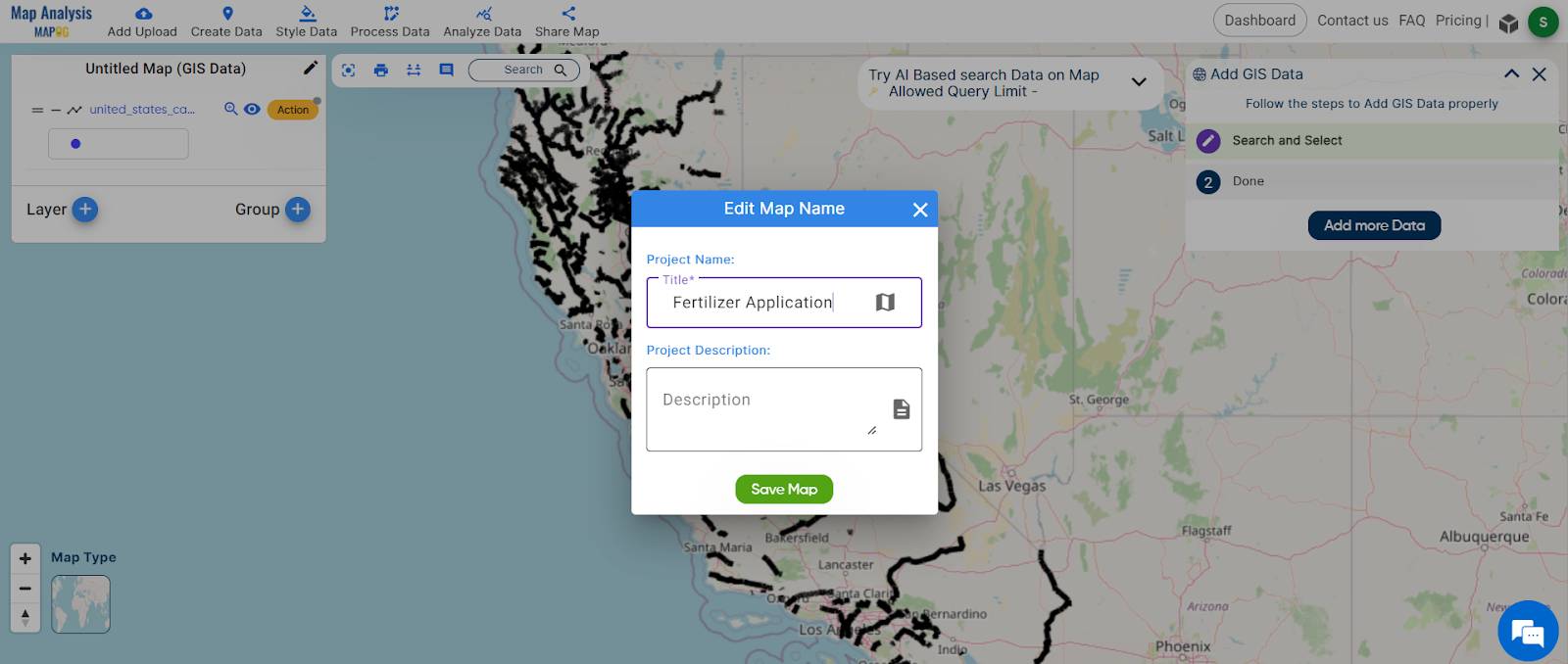
Step 2: Save and Rename Your Project
- Save your project by clicking the pencil icon above the action button, where you can also rename your project for better organization.
Step 3: Buffer Analysis
- Select Area of Study: After choosing the data layers and possibly cropping the area of interest, proceed to the designated area of study.
- Access Action Button of Agriculture polygon: Click on the action button associated with the Agriculture Data layer.
- Create Buffer: Within the actions menu, locate and select the option to “Create Buffer.”
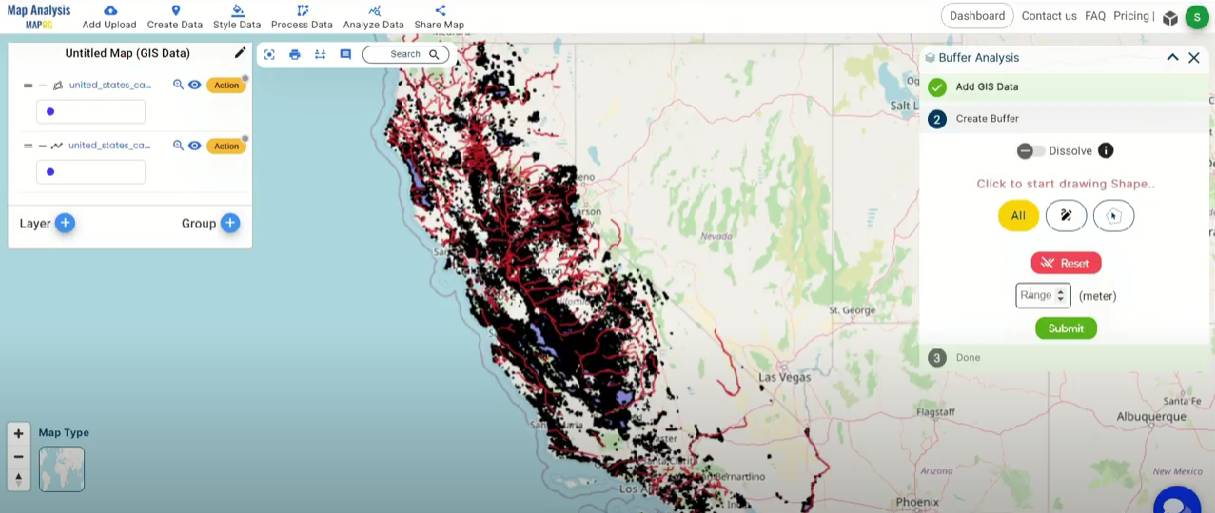
- Specify Buffer Zone: Input the desired buffer zone distance, in this case, 15 and 30 meters. Assign the range value as 15 in first buffer and 30 in second buffer.
- Submit: Once you’ve set the buffer parameters, click the “Submit” button to initiate the creation of the buffer zone.
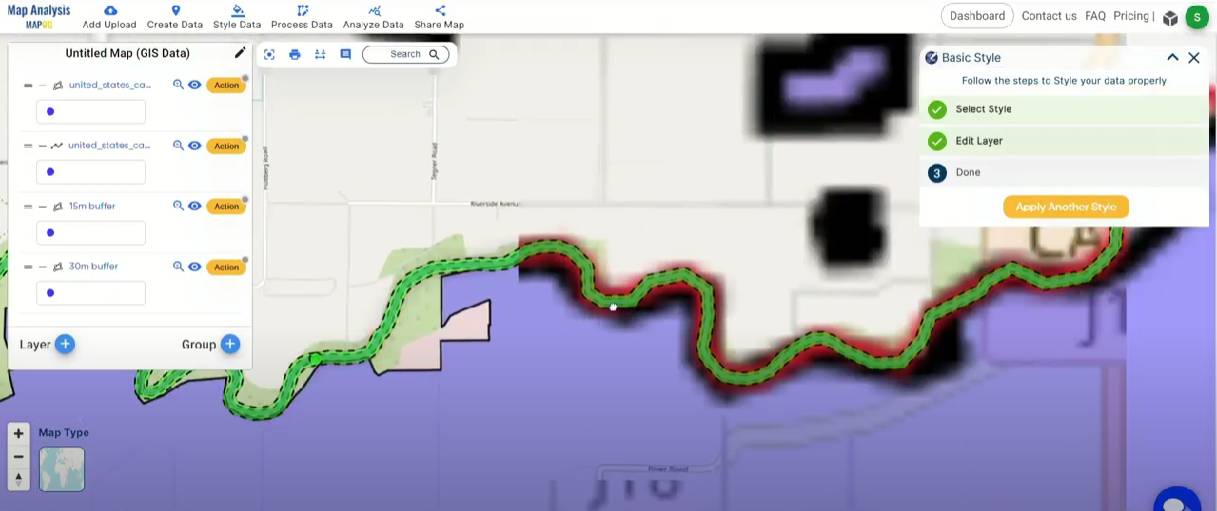
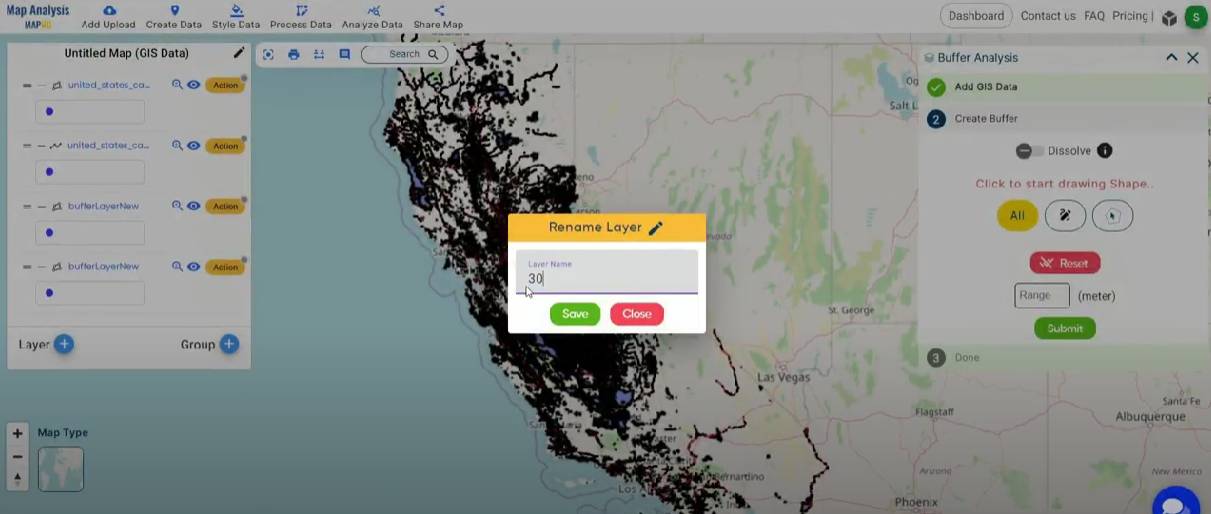
Step 4: Rename Layer
- Rename your layer by clicking the action button, then select the pencil icon to edit the layer name.
Major Findings
The application of the MAPOG Map Analysis for precision fertilizer application near water bodies has produced valuable spatial analyses. Establishing buffer zones around agricultural lands allows for a focused approach, optimizing nutrient management and adjusting fertilizer rates based on proximity to water resources. The precision provided by MAPOG ensures adherence to environmental regulations, acting proactively to mitigate potential environmental impacts. This fosters a sustainable coexistence between agriculture and water conservation.
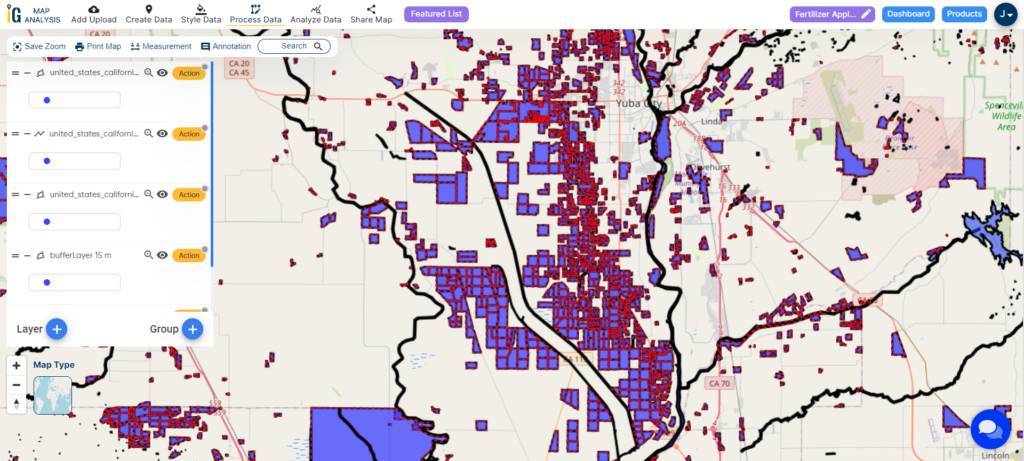
The results reveal a nuanced understanding of the relationship between farmlands and water bodies, emphasizing the significance of regulatory compliance and responsible resource management. Optimized nutrient application within buffer zones not only boosts crop yields but also contributes to the overall health of aquatic ecosystems by reducing the risk of water contamination. Successful case studies underscore the feasibility and advantages of adopting precision agriculture practices, showcasing the transformative impact of technology-driven, environmentally conscious farming practices.
Domain and Industry
- Agriculture and Farming: The primary domain is agriculture, specifically focusing on sustainable farming practices and precision fertilizer application.
- Environmental Technology: The use of MAPOG for spatial analysis aligns with the environmental technology domain, showcasing technology-driven solutions for sustainable agricultural practices.
- Data Analytics and Spatial Analysis: The industry involves data analytics and spatial analysis tools like MAPOG for making informed decisions in agriculture, emphasizing precision and environmental considerations.
- AgriTech: The use of technology, particularly MAPOG, places this within the AgriTech industry, showcasing the integration of technology for optimizing agricultural processes.
- Conservation and Water Management: The focus on creating buffer zones near water bodies indicates an intersection with the conservation and water management industry, emphasizing the responsible use of water resources in agriculture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the use of MAPOG for precision fertilizer practices near water bodies signifies a substantial move towards sustainable agriculture. The establishment of buffer zones showcases a targeted approach, optimizing nutrient management while considering water resource proximity. MAPOG‘s spatial precision ensures environmental compliance, proactively safeguarding against potential ecological impacts. This approach, emphasizing regulatory adherence and responsible resource management, not only supports robust crop yields but also contributes to the health of aquatic ecosystems by minimizing water contamination risks. The success stories in case studies underscore the feasibility and benefits of adopting precision agriculture, showcasing the transformative impact of technology-driven, environmentally conscious farming. For further inquiries or support, reach out to support@mapog.com, and explore how MAPOG can revolutionize traditional agricultural practices, fostering a more sustainable future.
GIS data links
- Download California Rivers GIS Data
- Download California Lakes GIS Data
- Download California Agricultural Polygon GIS Data
Other Articles
- Create Population Density Map : Add WMS Data
- Crime Data Mapping: Finding Patterns and Trends Using GIS
- Create Map for Landfill Optimization: Spatial Analysis Approach
- Fast Emergency Response: Using GIS and Isochrone Maps for 10-Minute Ambulance Arrival
- Mapping Tiger Attack Hotspots – Create an Online Map and Share
- Make Routes for Military Aerial Planning- Through Bearing angle and Distance calculation – Online Route Compass
- Mapping Healthcare Efficiency: GIS Buffer Analysis of Hospital Locations
- Add WMS- Two step online view of WMS layer on a map
- Plot ATM locations on a map and embed on your website
- Map habitat locations of endangered animals & keep track of their living