As electric vehicles (EVs) become more common on our roads, ensuring easy access to charging infrastructure is essential for a seamless driving experience. Drivers often face challenges in locating nearby charging stations, especially in unfamiliar areas or during long trips. Limited visibility and poor planning can lead to range anxiety and inconvenience. With MAPOG, mapping Electric Vehicle Charging Stations and locate it efficiently, visualize station density, and plan optimal routes empowering smarter travel and supporting the shift to cleaner, sustainable mobility.
Key Concepts
Mapping electric vehicle charging stations using GIS goes beyond pinpointing locations on a map; it’s about building an intelligent spatial network for cleaner, more efficient transportation. With MAPOG, users can identify charging station clusters, analyze accessibility based on driving range, and uncover coverage gaps. This spatial insight supports better city planning, enhances driver convenience, and drives the growth of sustainable mobility ecosystems.
Steps in Mapping Electric Vehicle Charging Stations:
1. Access MAPOG’s Mapping Platform
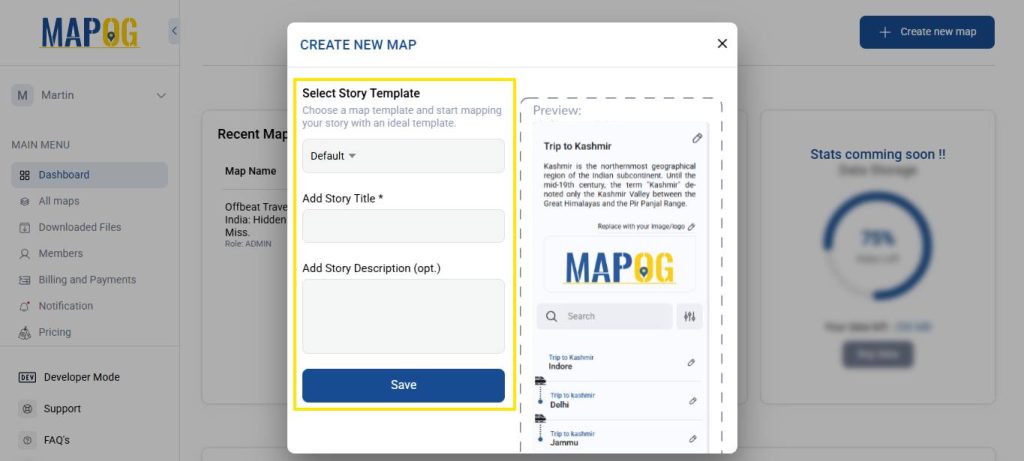
Visit MAPOG platform in your browser then, click on “Create New Map” in the top- right corner of the homepage to start creating your own map after that, add the title of your map. Description telling us what it’s about, then save.
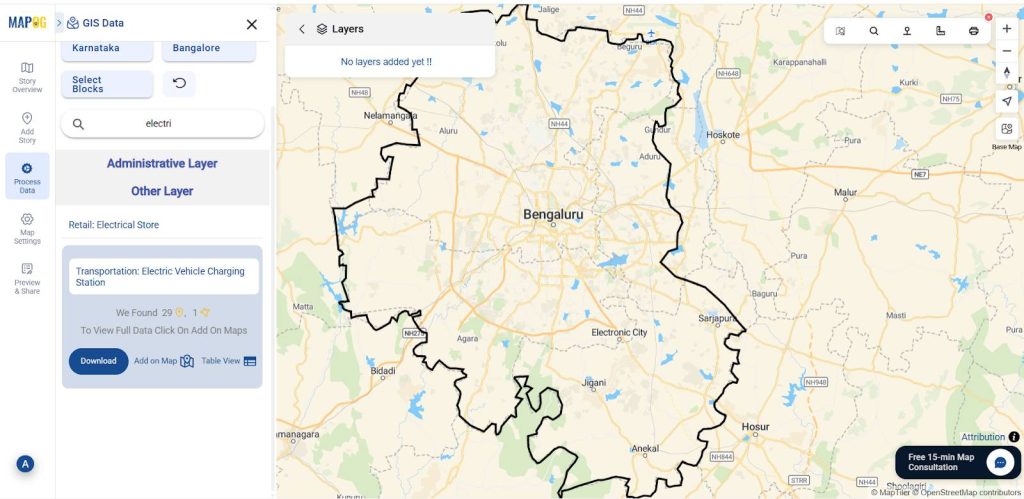
2. Add GIS Layers
After that upload the mention layers through the GIS Library from Process data.
Existing EV charging points→ For Demand, Coverage.
Commercial Area → Heavy usage
Parking Lot → Ample time
Shopping Mall → Easy charging
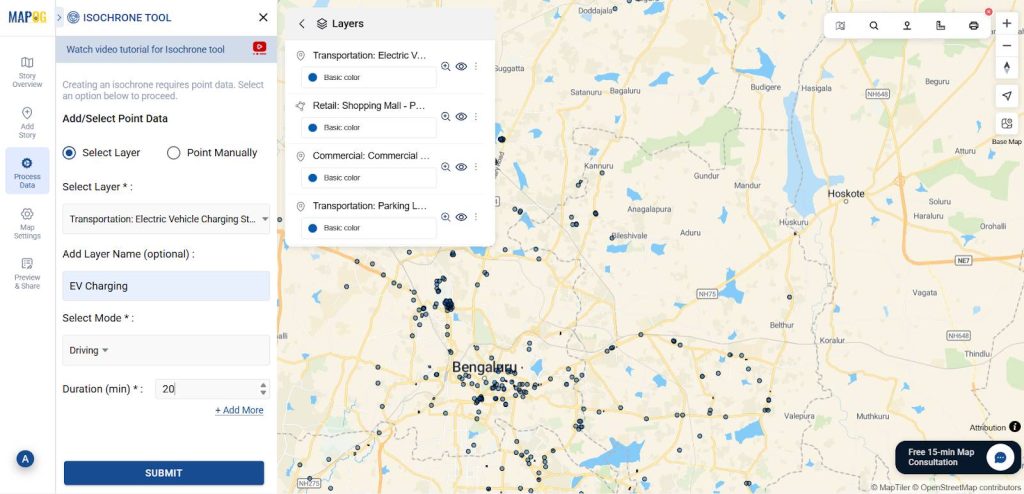
3. Perfoming Isochrone analysis
Then go to the “Process data” and select the “Isochrone Tool.” In the “Select Layer” option, choose EV Charging Station Location then, set the duration to 20 minutes and then click Submit.
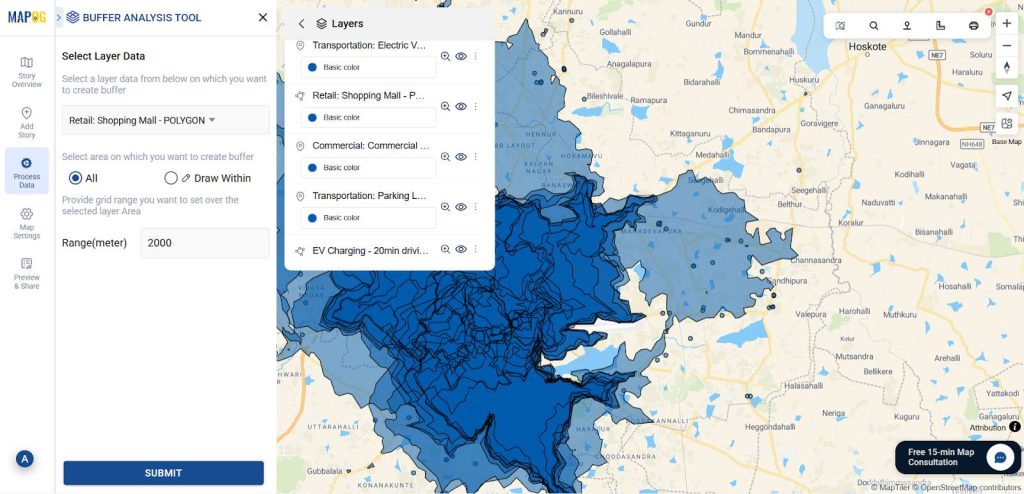
4. Performing Buffer Analysis
After that go to the process data and select the buffer tool. In the select layer data option select retail shop location set range as 2000 m the give submit. Follow the same process for other layers.
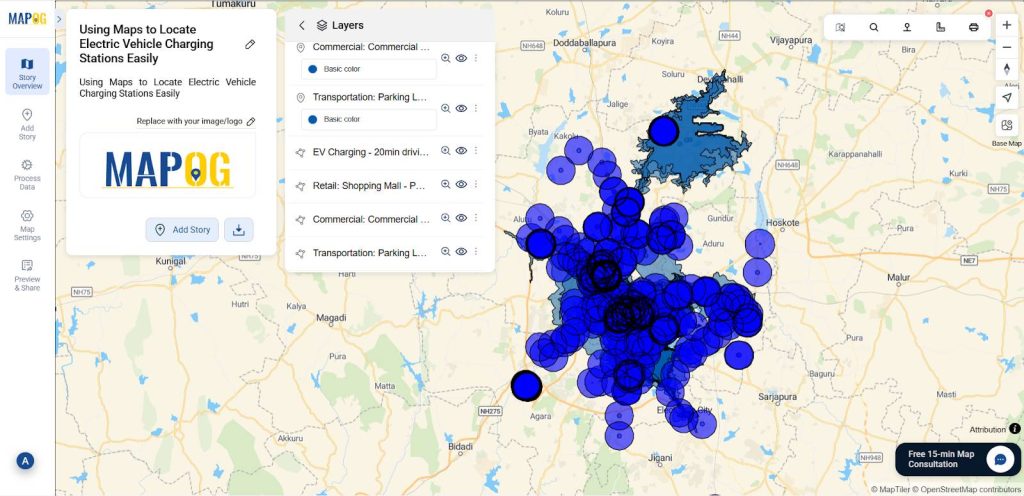
7. Customize buffer for Visual Appeal
You can change the interior colour and border colour of the buffer zones using the style layer.
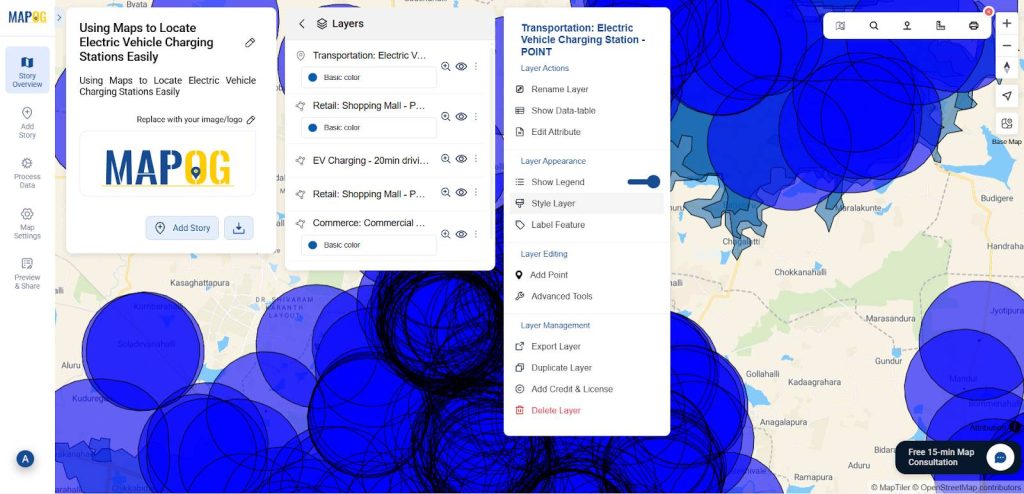
5. Add EV Charging Points Manually
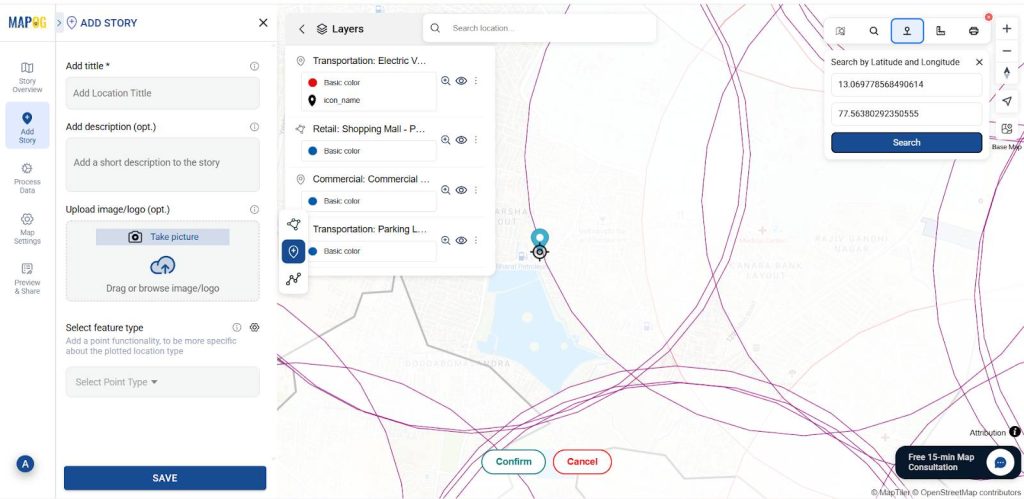
Now, use the “Add story” then select “add manually” then create EV charging points inside the buffer zone and outside of the isochrone, then select EV Charging point by using Search by Latitude and Longitude and give conform to confirm your selection. Then give the title for your point, write a short description about it, and upload a suitable image.
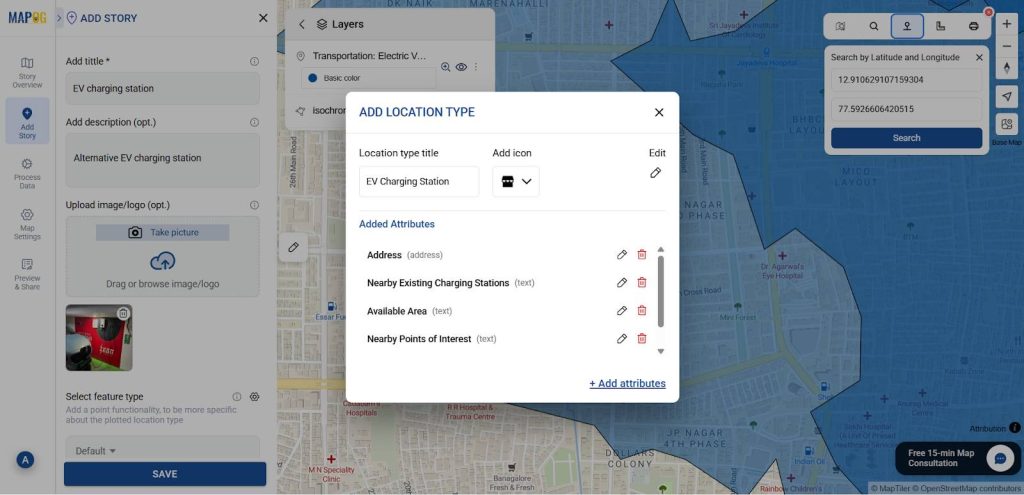
Using the select feature type settings option, add location type such as “EV Charging Stations” & add different relatable attributes to it, and later fill all the information there.
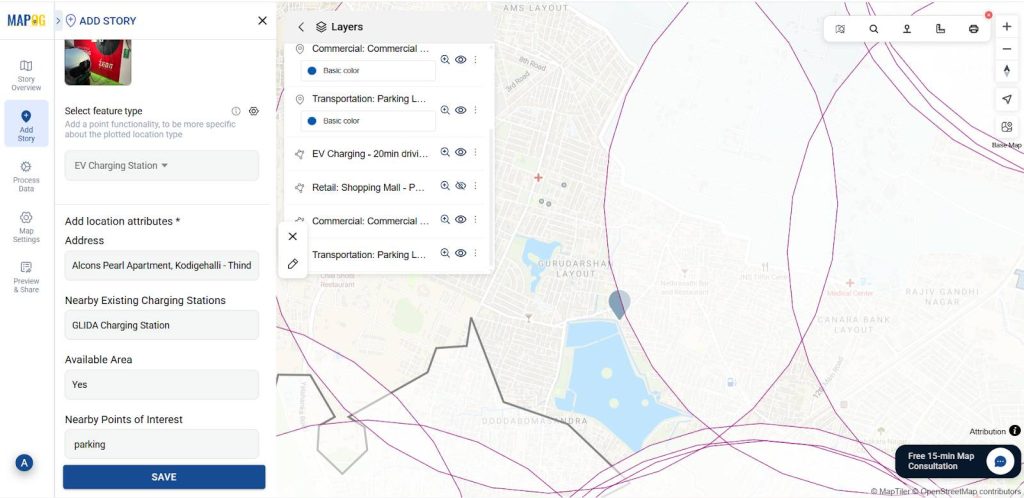
7. Customize Points for Visual Appeal
After that, label Electric Vehicle Charging Stations and customize icons with symbols using Point customization.
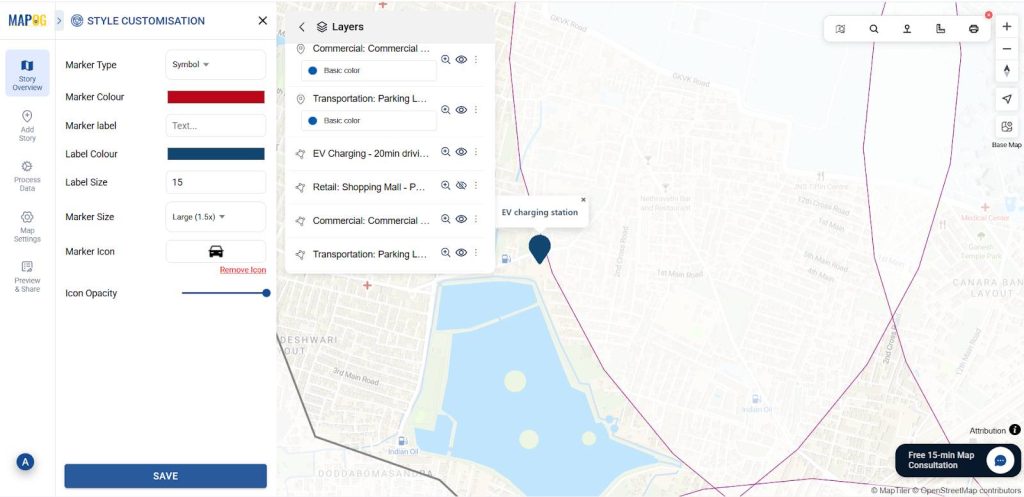
Then, follow the same procedure to add more EV Charging points.
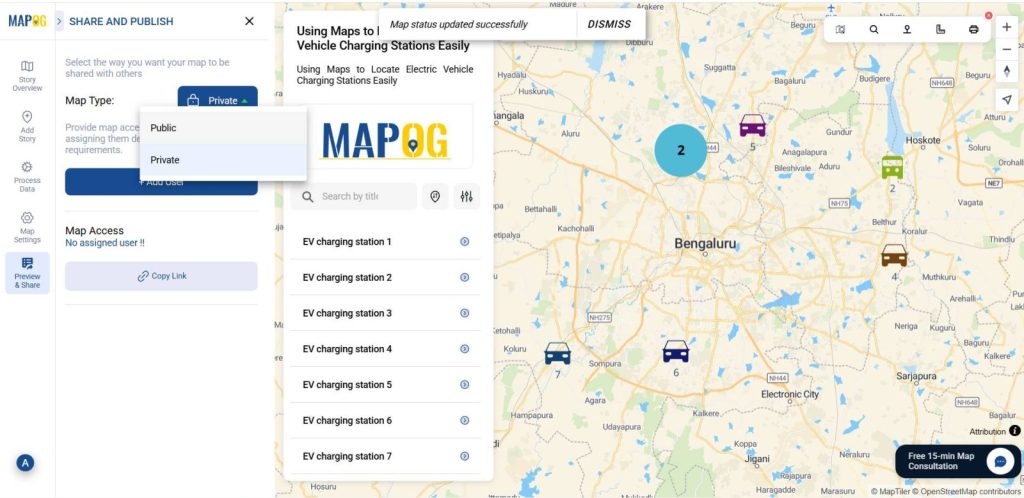
7. Share or Embed the Map Anywhere
Then go to the ‘Preview and Share‘ option, you can keep it private or change the map type to ‘Public’. This will enable the share link.
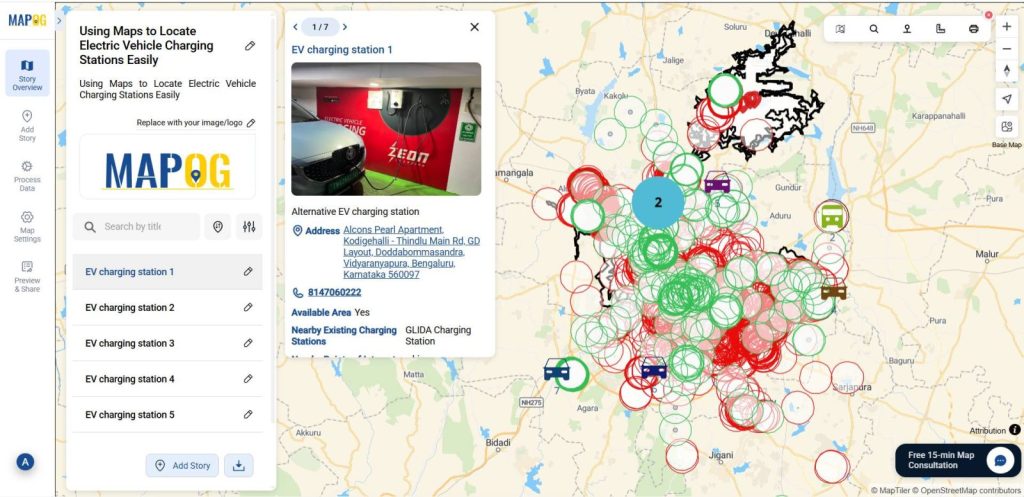
Finally we got the Alternative EV Charging stations map.
Who Can Take Advantage of Mapping Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Using Maps
Urban planners can use maps and data to find areas that lack charging stations and plan new ones so every neighborhood has fair access.
Transport departments can study travel patterns to place stations in the best spots, making long trips easier for EV users.
EV service providers can track how often stations are used, decide where to add more, and improve the overall charging experience.
Data Used
Transportation: Electric Vehicle Charging Station
Retail: Shopping mall
Transportation: Parking lot
Commerce: Commercial area
Conclusion:
Mapping EV charging stations becomes not only seamless but also highly effective with the power of MAPOG. By using this platform, you can easily visualize station accessibility, and moreover, identify underserved areas. In addition, you can optimize charging infrastructure, thereby enabling urban planners, transport authorities, and EV users alike to make smarter, data-driven decisions.
Here are articles related to this topic: