Mapping borewell locations near rivers and lakes is not only vital for understanding groundwater dependencies but also essential for ensuring sustainable usage. In fact, in regions where surface water and groundwater interact closely, analyzing borewell proximity to these natural water bodies becomes even more crucial. Moreover, with the help of GIS-based tools like MAPOG, users can easily visualize, GIS In Irrigation Planning and Water Resource Management.
Key Concepts
- Irrigation Suitability Mapping – Identify ideal areas based on soil, slope, and water sources.
- Water Source Mapping – Plot borewells, rivers, and reservoirs for better planning.
- Efficient Network Design – Use GIS to optimize canal and drip system layouts.
- Water Demand Estimation – Calculate crop water needs with spatial overlays.
- Recharge Zone Identification – Spot areas where groundwater can be naturally recharged.
- Drought Risk Mapping – Identify irrigation-stressed zones using rainfall and crop data.
- Real-Time Monitoring – Use GIS dashboards to track irrigation performance.
- Policy & Planning Support – Provide data-backed maps for smarter resource management.
Why GIS Is Essential for Mapping Borewells Locations Near Rivers and Lakes
By mapping borewell locations in relation to rivers and lakes, you can:
- First and foremost, identify zones at risk of over-extraction or contamination, which helps in prioritizing monitoring and regulatory action.
- Additionally, enhance water resource planning in both urban and rural settings, ensuring that development aligns with long-term groundwater sustainability.
- Moreover, evaluate the influence of surface water on groundwater recharge to understand aquifer health and natural replenishment dynamics.
- Finally, plan buffer zones and protection areas around key water sources to safeguard them from pollution and overuse.
How to Start Mapping Borewell Locations Near Rivers and Lakes
1.Prepare Borewell Data for GIS Mapping
First Start by creating an Excel sheet with the following fields:
- Location Name
- Latitude
- Longitude
- Depth (optional)
- Source (e.g., Groundwater)
2. Log in and Create a Project
Head to MAPOG, log in, and create a new project. Give it a title such as “Borewells Near Water Bodies – [Region Name]” and add a brief description.
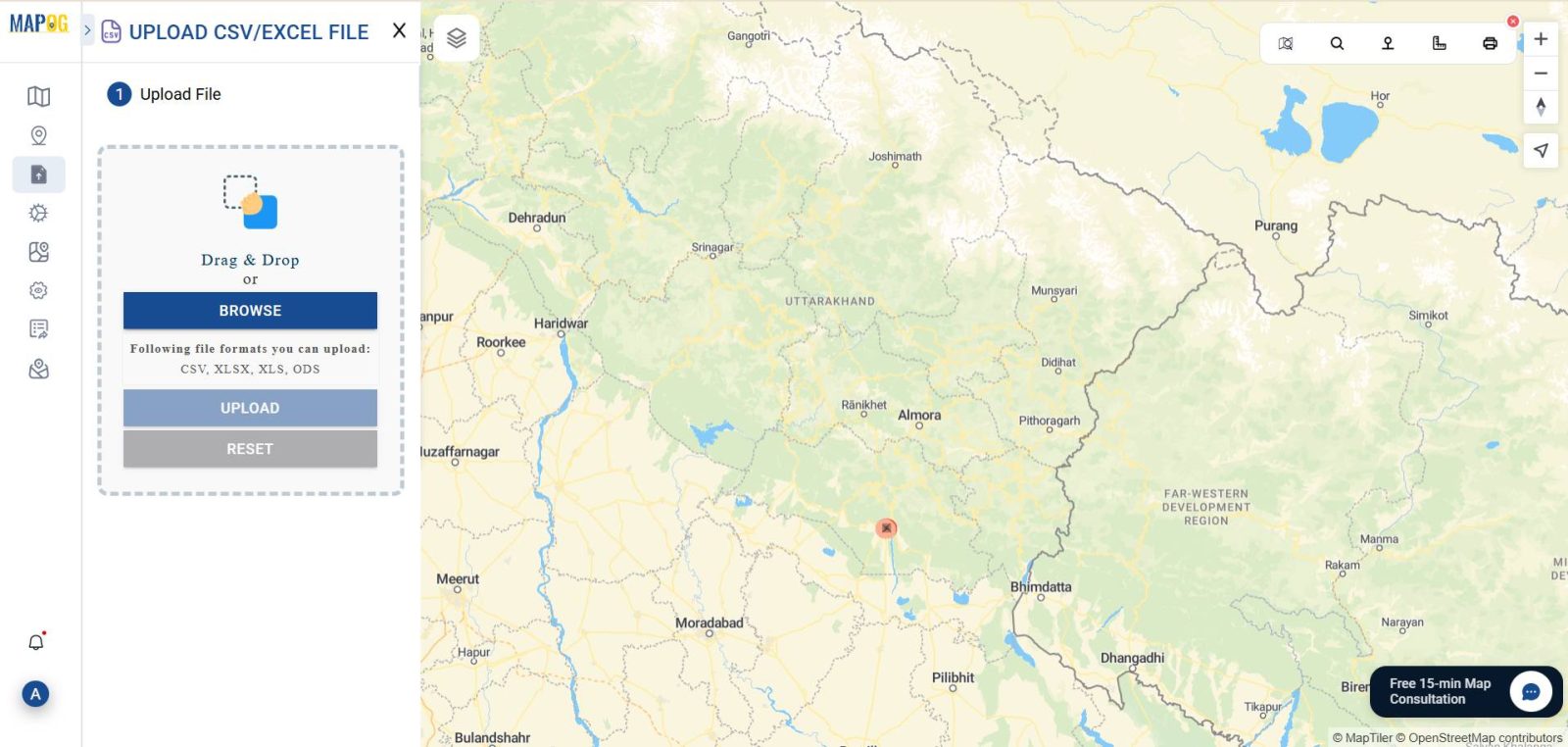
3. Upload Borewell Coordinates
Click on “Add Data” > “Upload CSV/Excel.”
- Select your Excel file
- Match the Latitude and Longitude columns during upload
- Complete the upload to visualize borewell points on your map
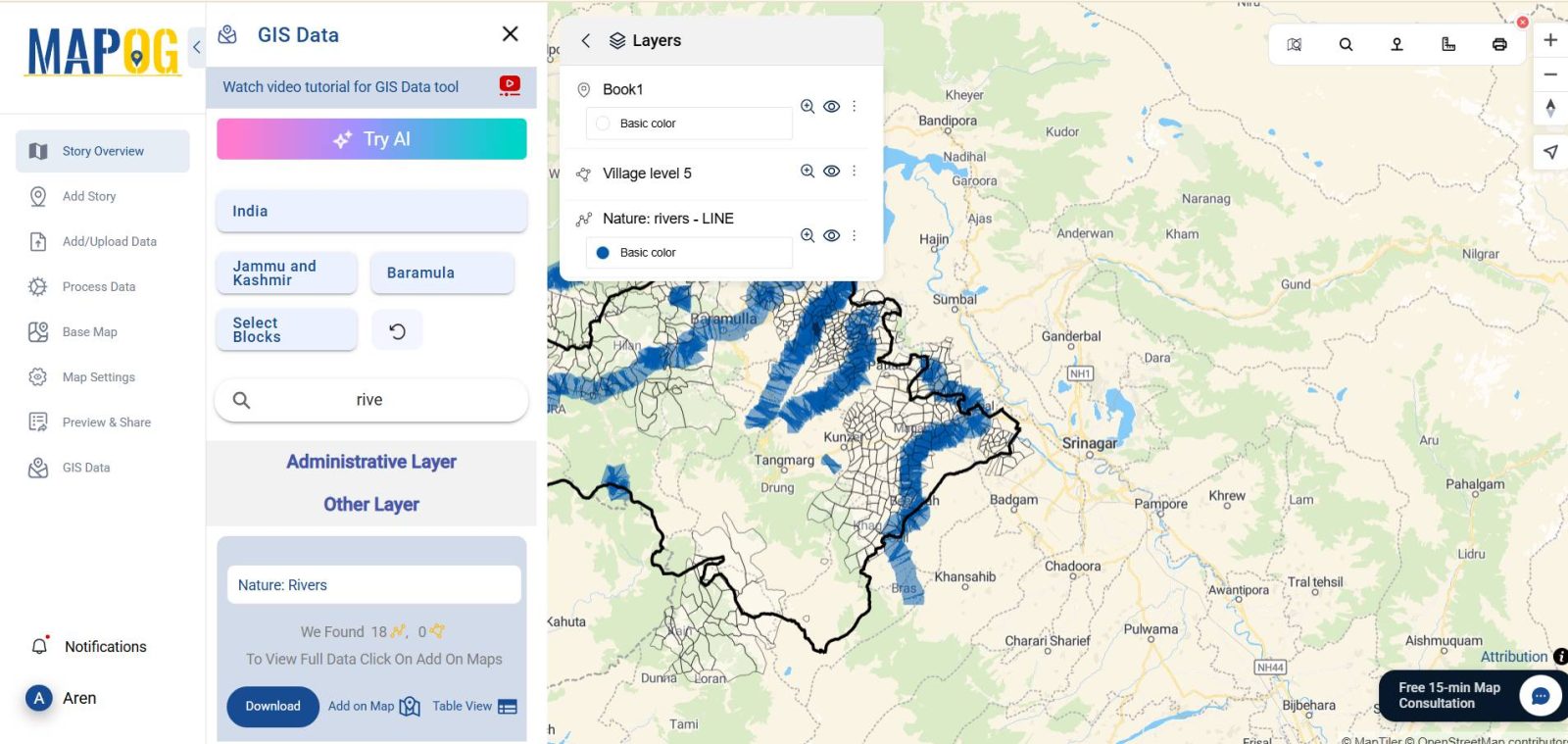
4. Add Water Body Layers from GIS Library
Next, enhance the map context by adding water bodies:
- Add a base layer such as district boundaries by using GIS Data.
- Search and add layers like Rivers, Lakes, or Water Bodies
- Ensure these layers are placed below your borewell layer for visibility
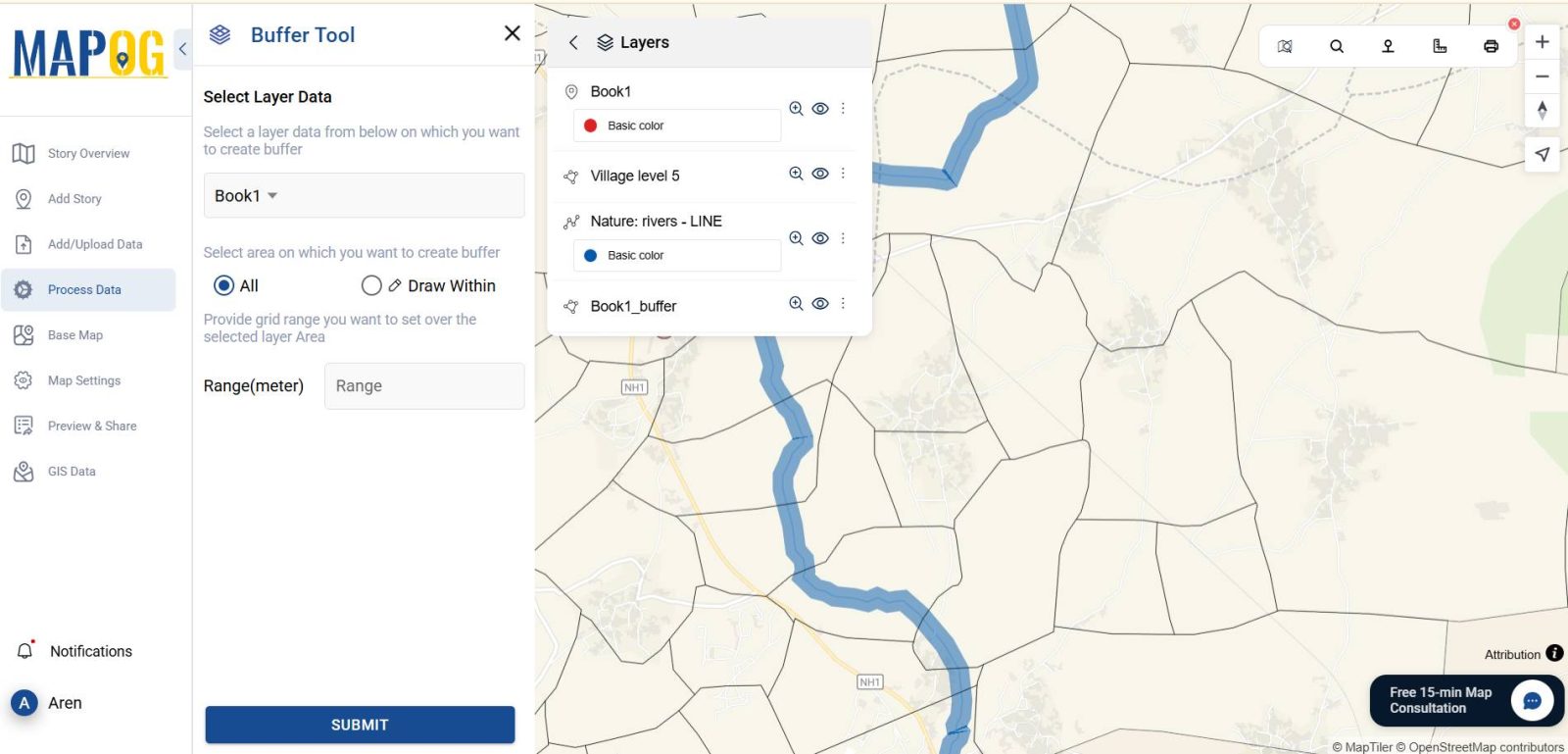
5. Create Buffer Zones Around Water Bodies
To analyze how close borewells are to rivers or lakes:
- Go to ” Buffer Tool”
- Choose the water body layer as your input
- Set the buffer radius (e.g., 300 meters)
- Style the buffer with transparent fill and outline
- Name the buffer layer, such as “Water Body Influence Zone”
6. Style the Borewell Layer for Better Insights
Navigate to “Style Layer”
- Use color to differentiate borewell sources or depth ranges
- Add labels to highlight specific wells or attributes
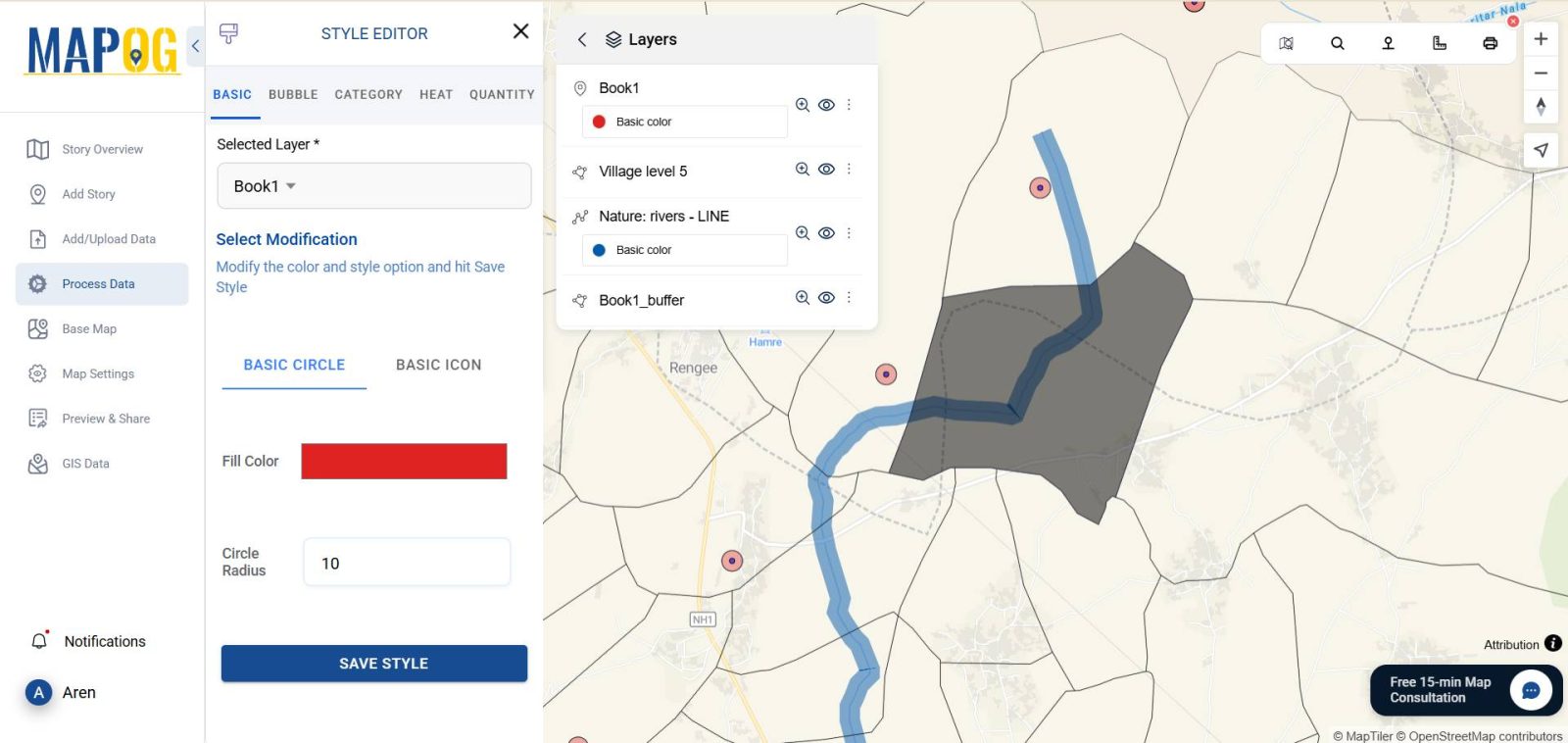
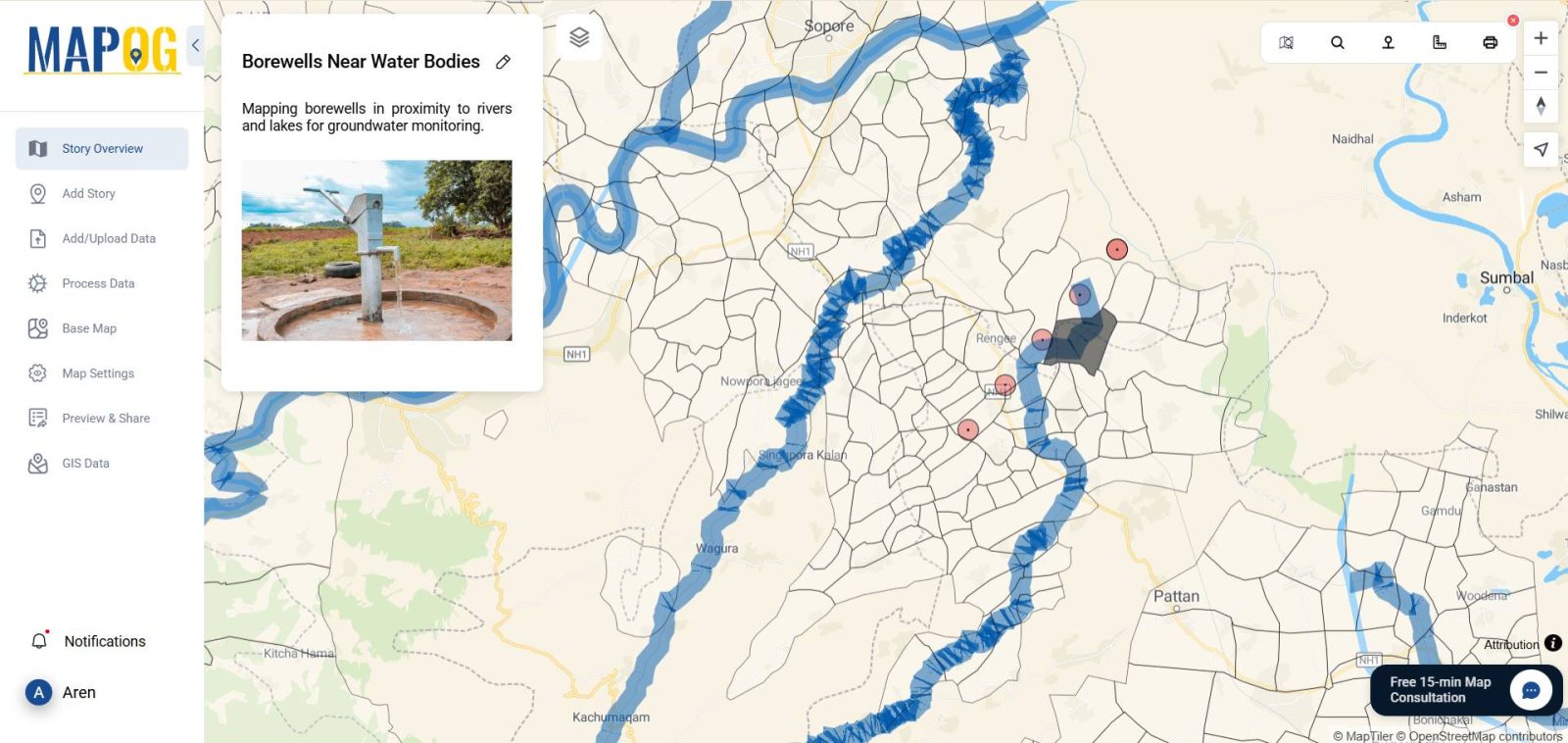
7. Analyzing Borewell Proximity with Buffer Zones
- Which borewells fall inside water body buffer zones
- Whether closer proximity correlates with higher recharge levels
- Any spatial clustering that may indicate overuse in certain areas
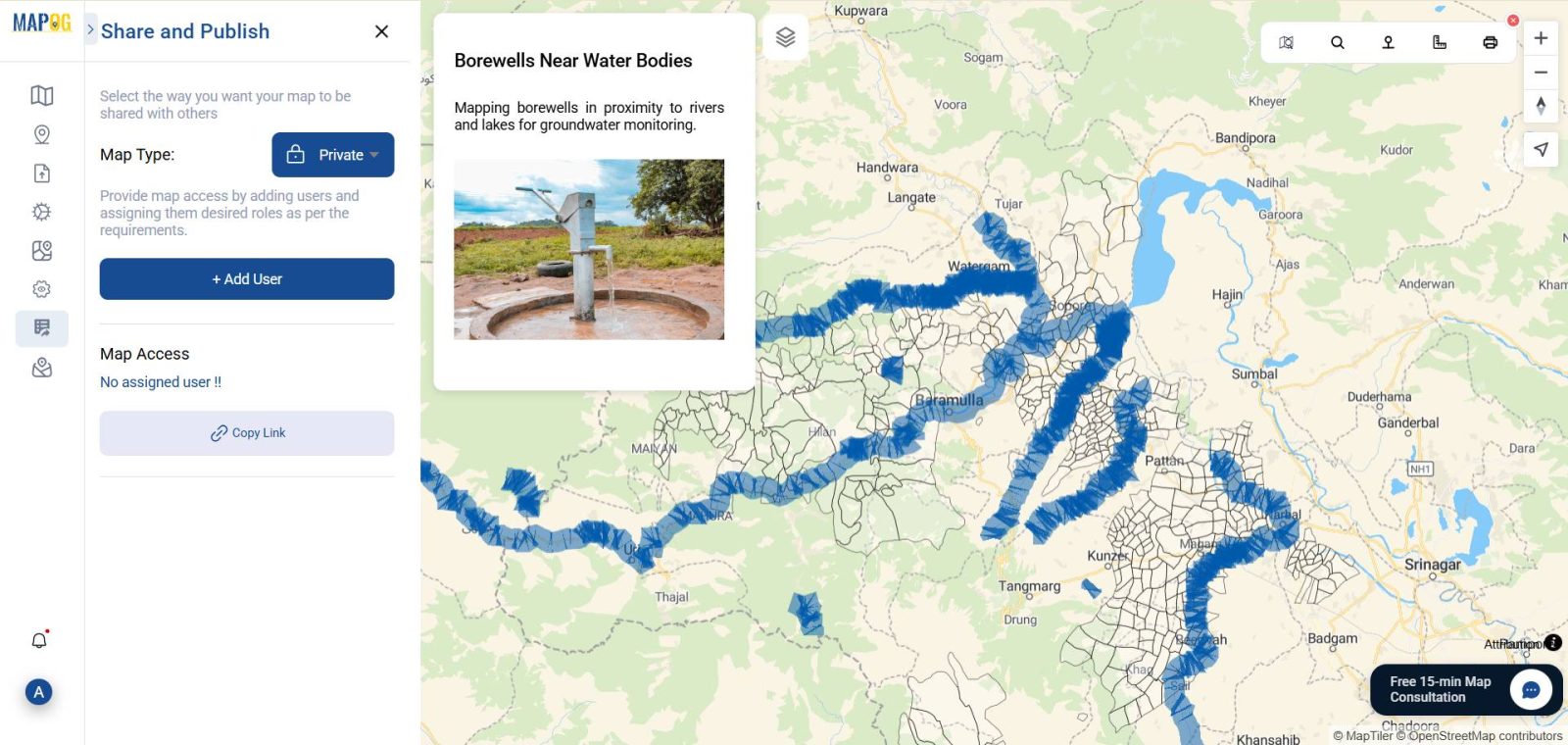
8. Sharing and Using Your GIS-Based Borewell Map
- Click “Share & Publish“
- Generate a public link or embed code
GIS DATA USED
Industry Applications and Relevance
- Mapping borewells near rivers and lakes using GIS is crucial across several sectors. To begin with, it plays a key role in urban planning by assisting municipalities in designing infrastructure that aligns with groundwater availability.
- In addition, it supports environmental conservation efforts by enabling NGOs and researchers to protect both aquatic ecosystems and groundwater reserves.
A Step Toward Water-Smart Futures
Mapping borewell locations near rivers and lakes using MAPOG equips stakeholders with accurate, actionable insights. This visual approach fosters smarter decisions, encourages water conservation, and ensures better regional planning.
Conclusion: The Value of Mapping Borewell Locations Near Rivers and Lakes
Mapping borewell locations near rivers and lakes using GIS tools not only empowers planners, environmentalists, and water managers but also enables them to visualize critical interactions between groundwater and surface water more effectively. Additionally, MAPOG simplifies the entire process by transforming complex datasets into clear, actionable maps.
Exploring Our Previous Blogs
You might also be interested in our insights on Creating a Responsive EV Charging Map and GIS in Infrastructure Development and Road Network Analysis, which show how spatial data helps shape sustainable cities.
- Role of GIS In Irrigation Planning and Water Resource Management
- How GIS and Smart Mapping Reduce Urban Heat Islands
- GIS in Infrastructure Development and Road Network Analysis
- Flood Risk Mapping with Interactive Web Maps: SaaS Approach
- Optimizing Warehouse Location Selection with GIS for Supply Chain Efficiency