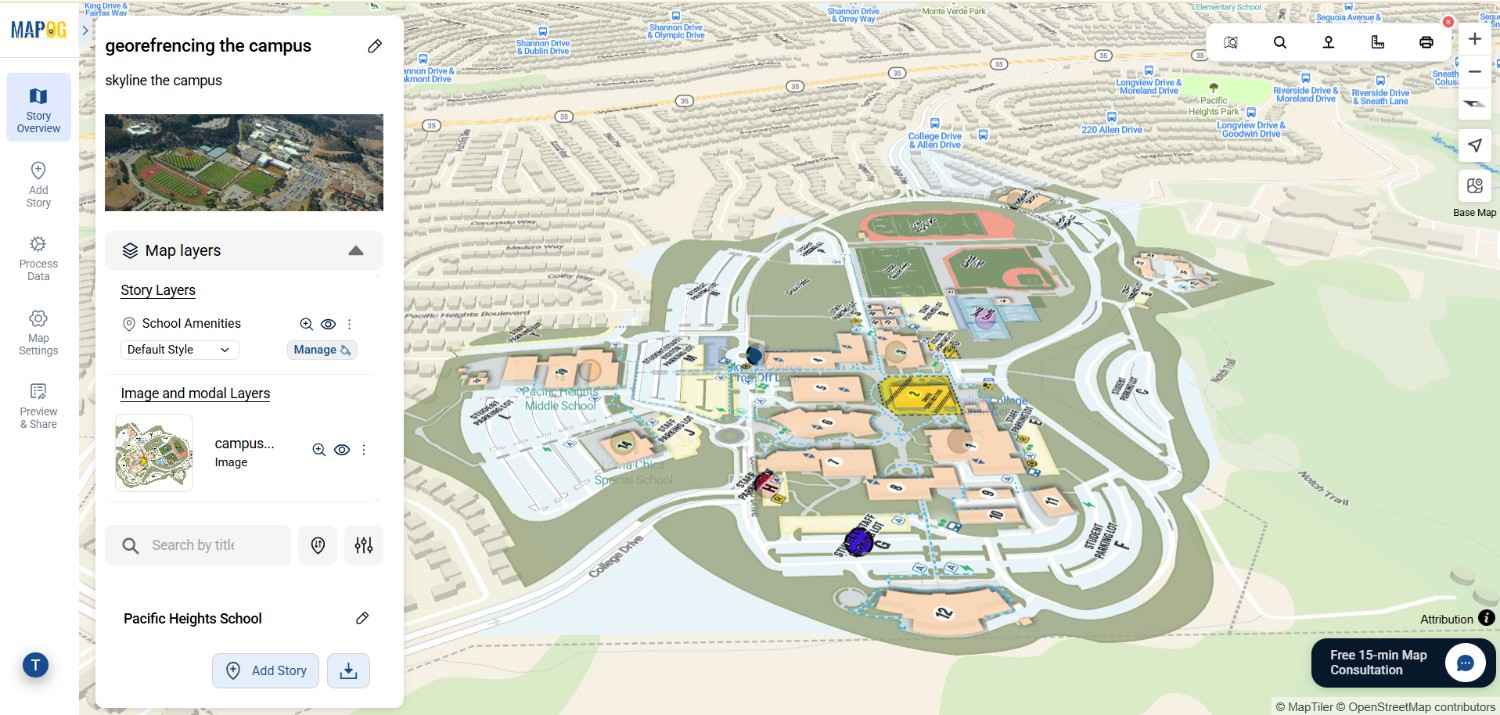
Adding georeferenced image overlays—such as PNGs or GeoTIFFs—to a map can be challenging. Especially when working with , georeference a base map image or custom visuals. The main difficulty lies in aligning the image with real-world locations so that landmarks and features appear at the correct scale and position.
While many GIS platforms support raster overlays, they often involve complex steps like handling file formats, projections, or coordinate systems. MAPOG simplifies this process.
Why Georeference a base map Image Overlays Matter in Mapping
Georeferenced image overlays play a crucial role in turning static visuals into spatially meaningful layers. Additionally this enable users to place campus maps, field sketches, or thematic illustrations onto a base map with geographic accuracy.
This capability enhances context, supports analysis, and helps communicate location-based insights effectively—especially in areas like planning, disaster response, or community mapping.
Steps to Add Georeferenced Image Overlays on a Map
1. Add Your PNG File
In MAPOG, after creating a new map, go to the “Add Story” section. From there, select “Georeferencing” to enable image overlay functionality.
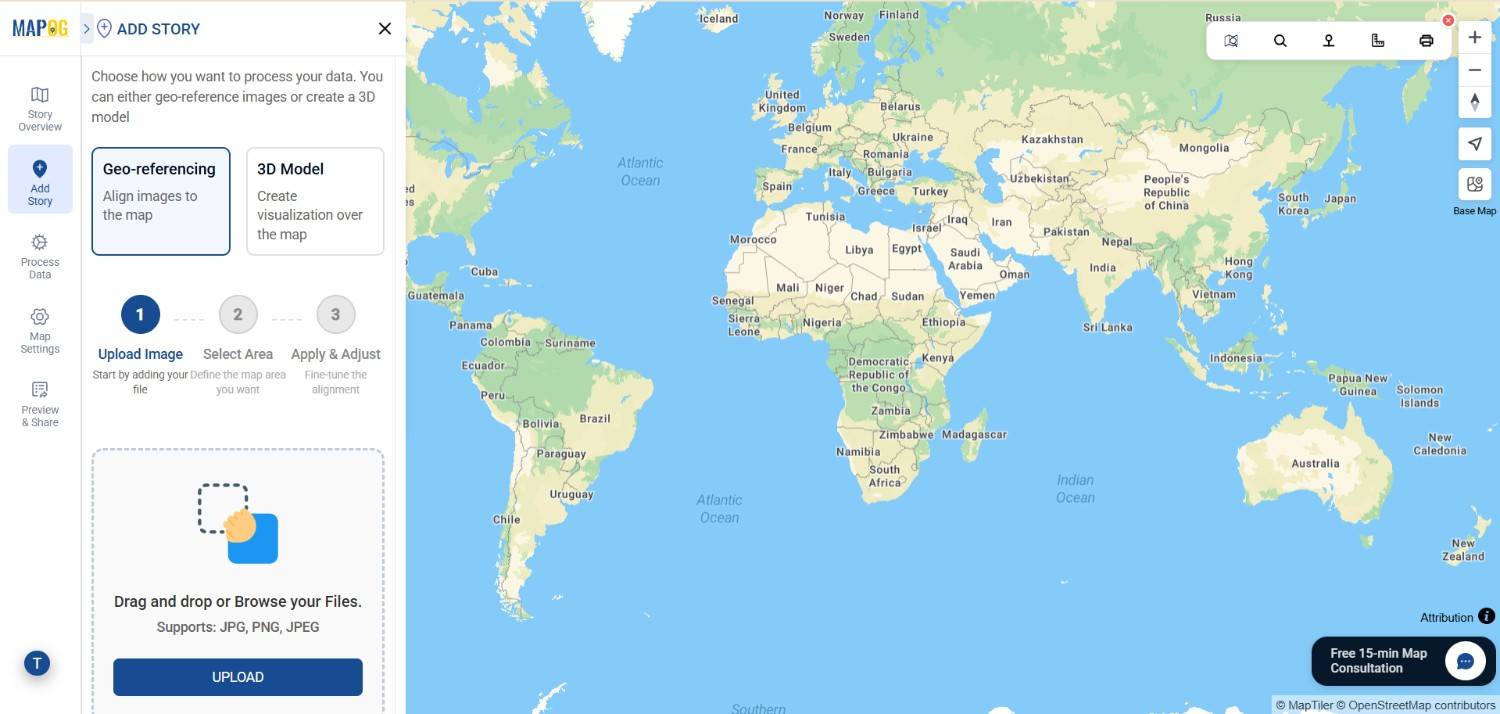
2. Upload Your Image
Click on the “Upload” button and choose your PNG or GeoTIFF file. Once uploaded, the image will appear on your workspace, ready for placement.
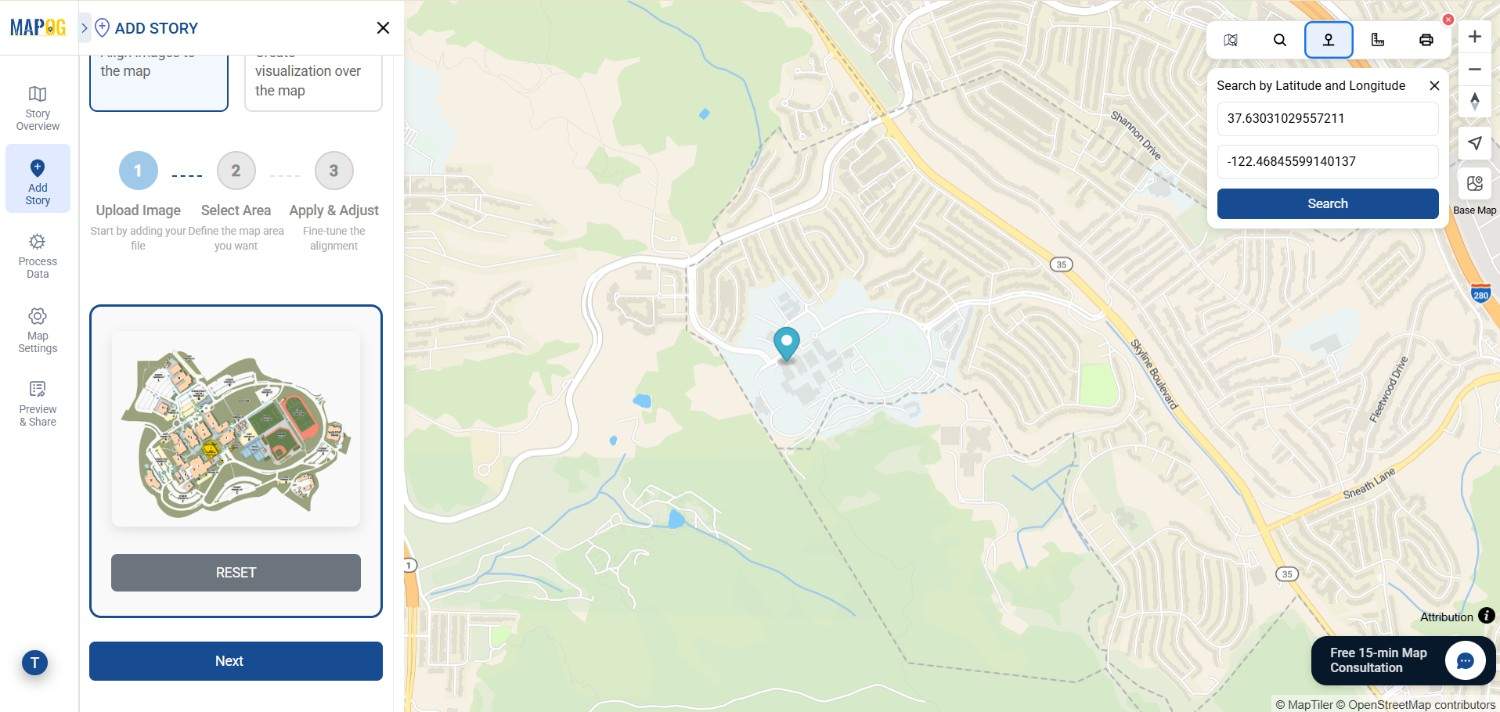
3. Search for Your Location of Interest
Before drawing, use the Search icon from the toolbox to locate the area where the image should be overlaid. This ensures you’re working within the correct geographic context.
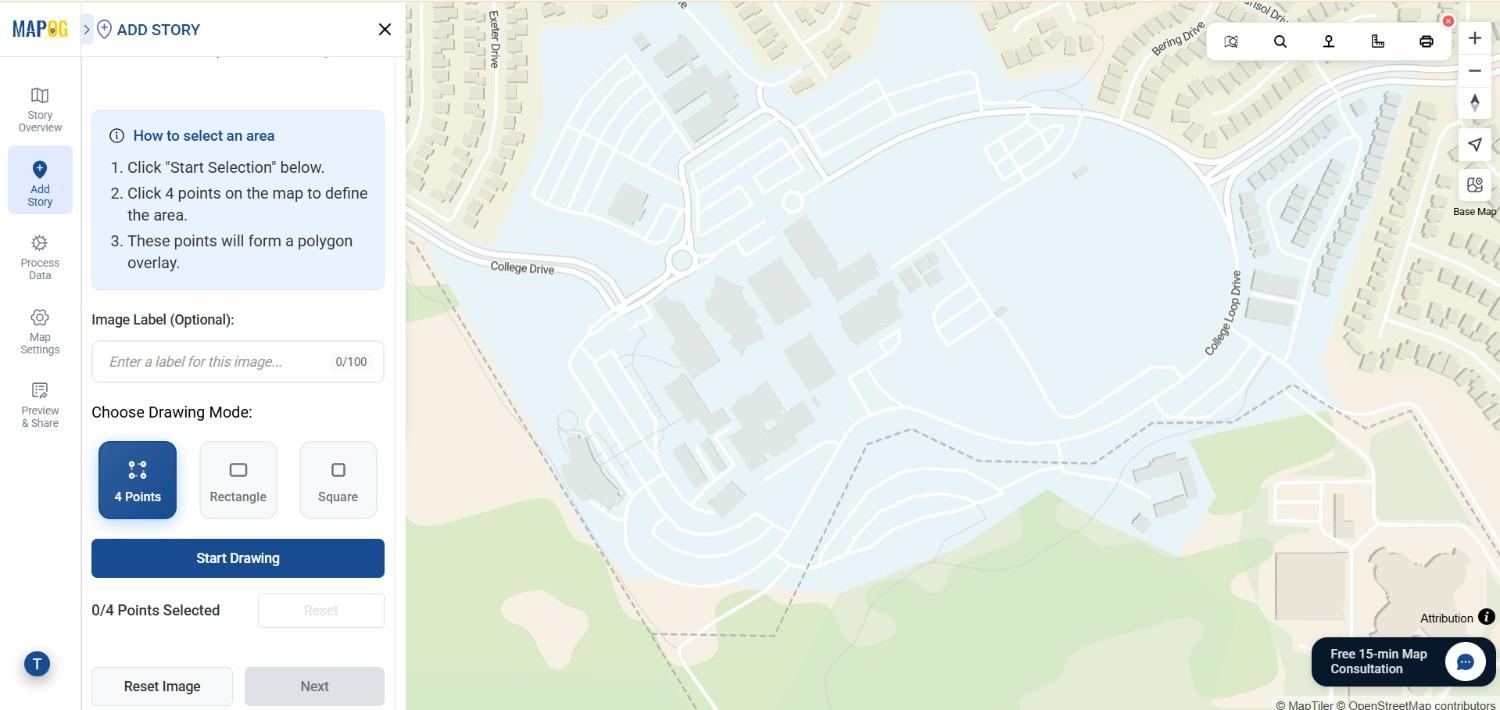
4. Choose a Drawing Mode
After confirming the location, click Next. Choose a drawing mode—“4 Points,” “Rectangle,” or “Square”—depending on how you want to anchor your image. Then click Start Drawing to continue.
5. Mark the Area on the Map
Select the region of interest where your PNG should be placed. This step defines the area within which the image overlay will appear.
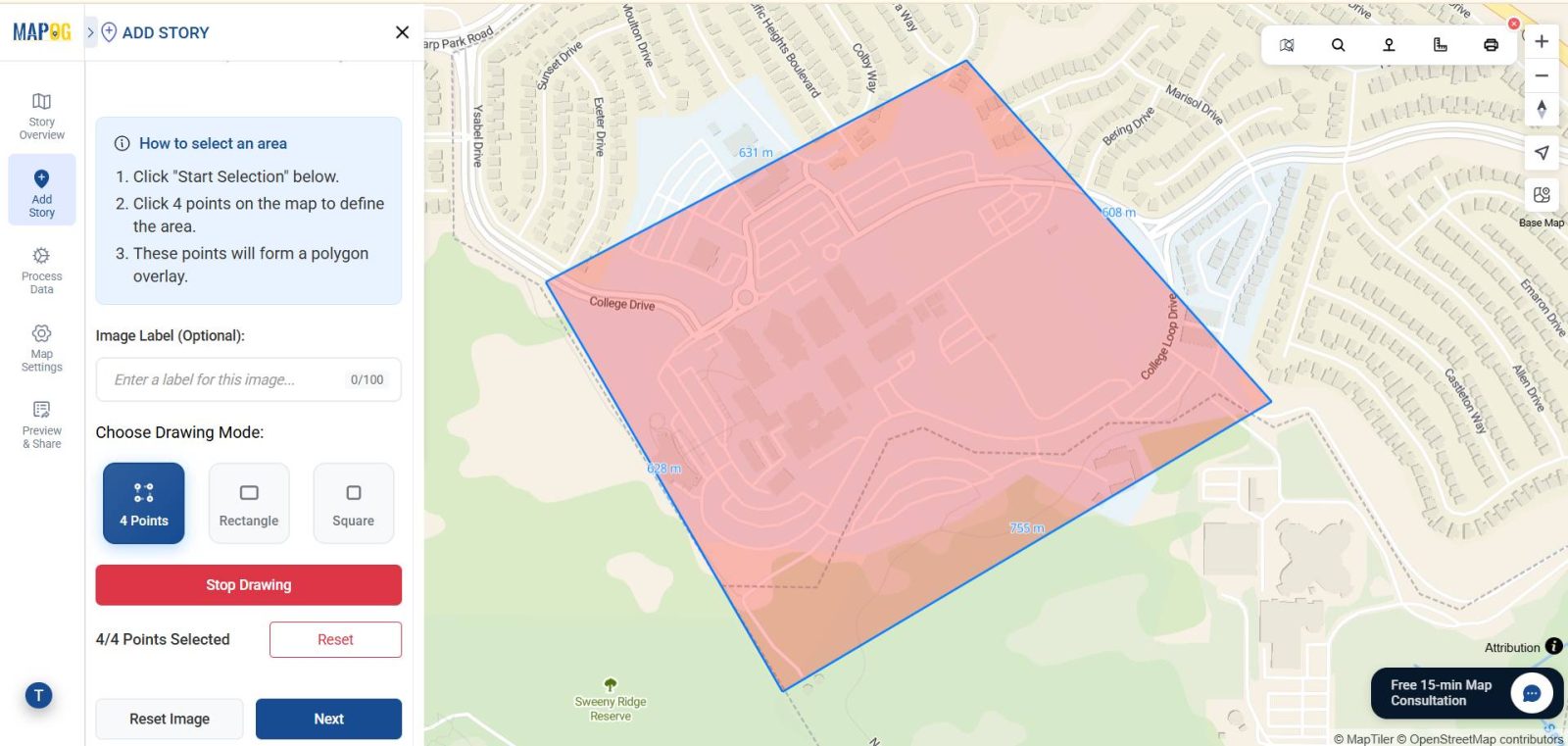
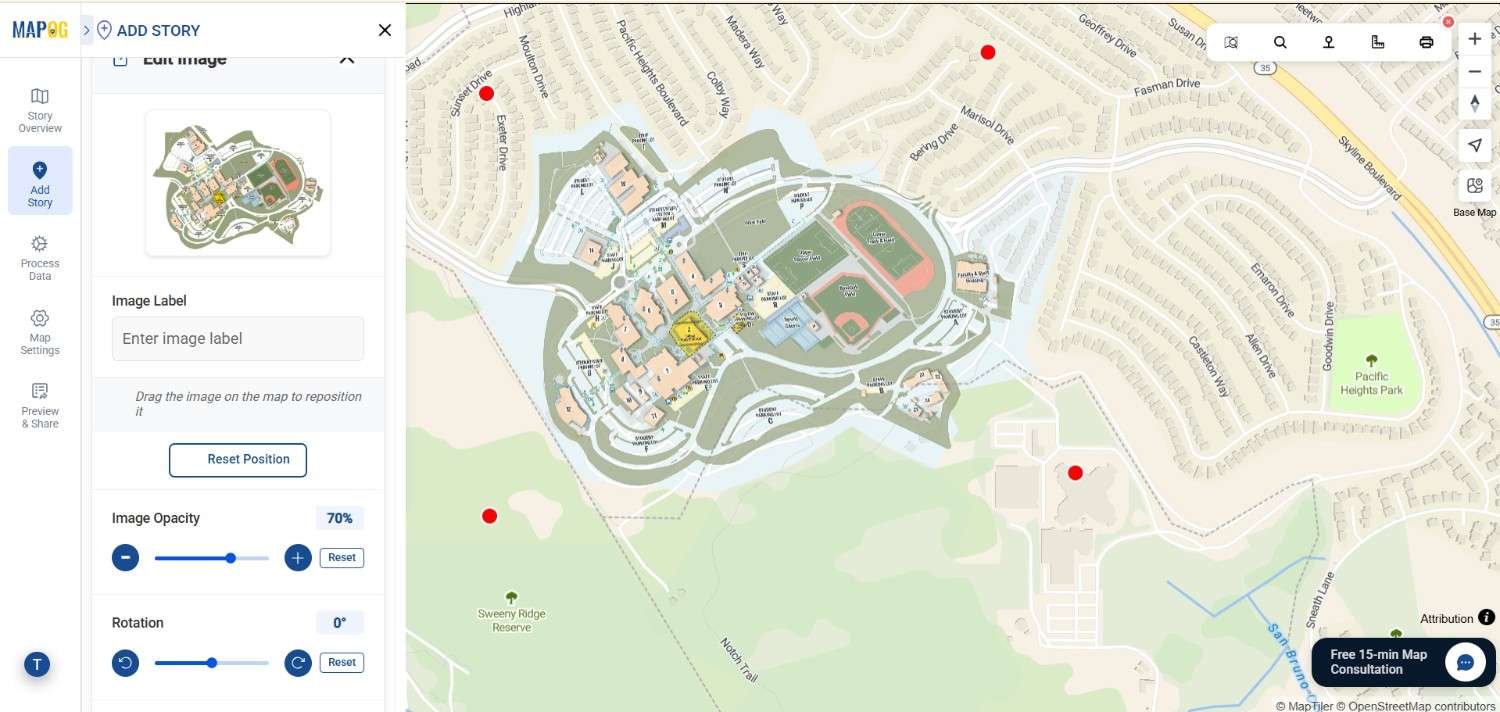
6. Align the PNG with the Basemap
Next, align your image with the actual basemap by matching key landmarks such as buildings, roads, or open spaces. Fine-tune the placement using the opacity slider, scale, and rotation tools until your image fits perfectly. Then, click Save.
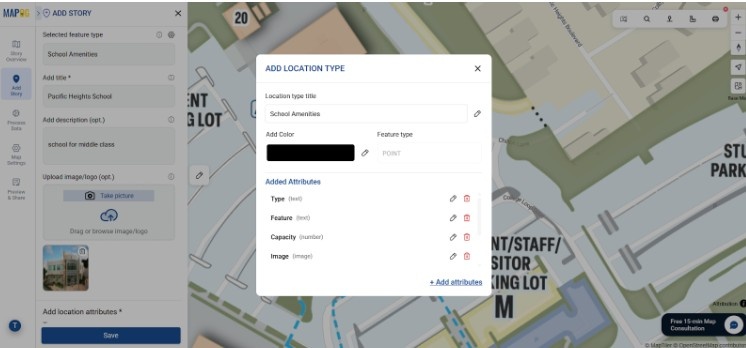
7. Add attributes
Lastly go to the Add Manually and start adding points, lines, or polygons to mark features such as departments, hostels, roads, or green zones. In each point add attributes by Going to Select feature type Settings, create a new location management type. Additionally Provide title, icon & feature type (point) to that. Add attributes like name , type etc to make your map informative and actionable. Lastly save the location type .
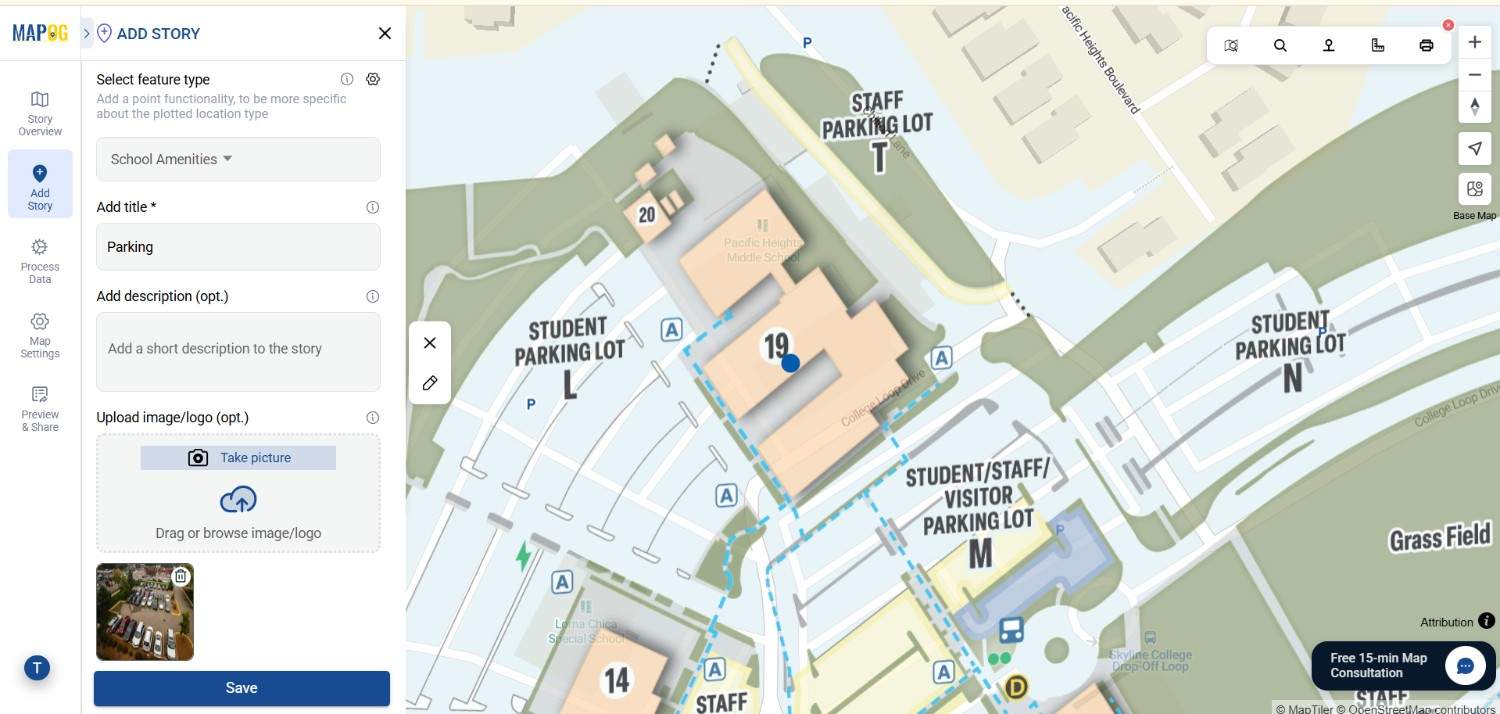
8. Save the map
After adding the attributes you confirmed the location, add information & image and then now similarly add different locations and save the map .
Industrial Use and Benefits of georeference a base map image
Urban Planning and Campus Development:
To begin with, planners can overlay campus layouts or zoning maps to assess expansion, visualize accessibility, and monitor service coverage effectively. In addition, these overlays allow authorities to compare existing infrastructure with proposed developments, ensuring informed planning decisions.
Disaster Management and Risk Mapping:
Furthermore, during emergencies, response teams use flood extent GeoTIFFs or hazard zone PNGs to identify risks, plan evacuations, and guide recovery operations efficiently. In the same way, these overlays reveal how hazard zones overlap with population centers, improving disaster preparedness.
Environmental Monitoring and Agriculture:
Meanwhile, researchers track vegetation health, soil types, and land-use changes to promote sustainable resource management. Additionally, by comparing georeferenced layers over time, they can detect environmental degradation and support conservation efforts.
Healthcare and Public Services:
Lastly, health departments overlay facility layouts and service zones to locate underserved regions and optimize response times. Moreover, such overlays help planners evaluate how population density affects accessibility, leading to better infrastructure distribution.
Conclusion
Georeferencing image overlays like PNGs and GeoTIFFs provide a practical way to connect static visuals with real-world geography. Through MAPOG’s intuitive workflow, users can upload, position, and adjust overlays using simple tools like drawing modes, search.
Exploring Our Previous Blogs
- Role of GIS In Irrigation Planning and Water Resource Management
- How GIS and Smart Mapping Reduce Urban Heat Islands
- GIS in Infrastructure Development and Road Network Analysis
- Flood Risk Mapping with Interactive Web Maps: SaaS Approach
- Optimizing Warehouse Location Selection with GIS for Supply Chain Efficiency